
The relation that determines the circulation of the airfoil: the Kutta condition (making the flow smooth at the trailing edge) Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDĬoordinate transformation: Solution is given by: Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDĬalculation of the lift: Lift coefficient: Lift slope: Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDġ6 The symmetrical airfoil: pitching momentĬalculation of the pitching moment about the leading edge: Moment coefficient about leading edge: Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUD
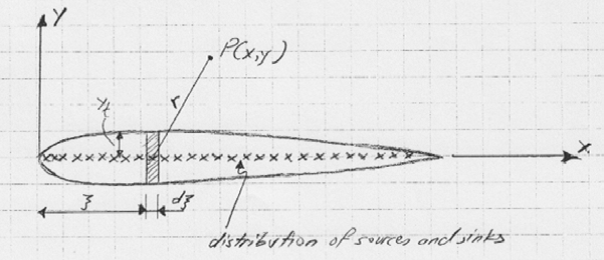

The fundamental equation of the thin airfoil theory: the flow-tangency condition (making the camber line z(x) a streamline) 2. Normal component of the freestream slope of the camber line velocity induced by the vortex sheet (x is fixed is running variable) Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDġ1 Resume: the basic equations of the thin airfoil theoryġ. with large aspect ratio) V Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDĪttached flow: cl ~ a (inviscid) airfoil theory Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUDĥ Limitations of the (inviscid) airfoil theoryĪssumptions: - inviscid, irrotational flow - incompressible What is correctly predicted: the pressure distribution over the airfoil lift and pitching moment What is absent: viscous effects: - boundary layer development friction forces flow separation no prediction of drag (D = 0!) or maximum lift Conclusion: airfoil theory can reasonably predict lift and pitching moment as long as the flow does not separate Aerodynamics-B, AE2-115 I, Chapter 4 Gerritsma & Van Oudheusden TUD Prandtl’s approach to the analysis of airplane wings: (1) the study of the section of the wing (the airfoil) (2) the modification of airfoil properties to account for the complete wing z What is an airfoil? an “infinite” wing in 2D flow the local section of a true wing x y Airfoil section Motivation for looking at airfoils: the wing properties follow from the local airfoil properties a good model for slender wings (i.e.

Presentation on theme: "The concept of the airfoil (wing section)"- Presentation transcript:ġ The concept of the airfoil (wing section)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
